Belt drive fans have two additional bearings.
Direct drive versus belt driven fans.
More often than not the maintenance cost of this kind of fan is also comparatively lower.
Direct drive fans should be designed for acceptable bearing life.
The second pulley is connected to a shaft that drives the fan propeller.
Deciding between a direct drive fan and a belt drive fan is fairly straightforward once you know all of your other variables like fan size application space fan speed needs and likely wear and tear in your application.
It s a motor connected to your fan in one of only two ways.
Where on a belt drive fan the fan motor shaft has a pulley connected by a belt to a second pulley.
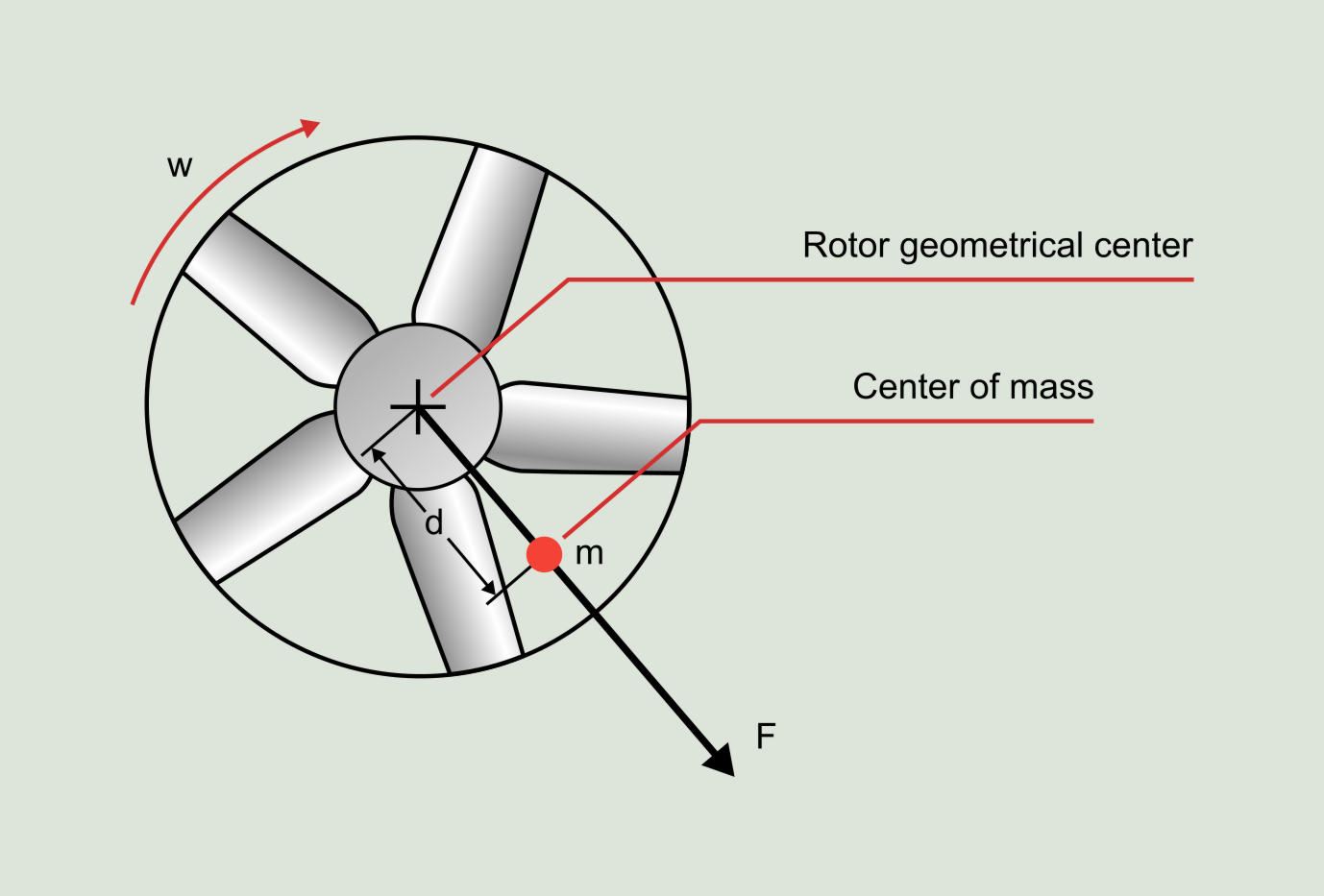
In a direct drive configuration the fan motor that controls the movement of the fan blades is connected either to a shaft or fan axle.
Thus the fan blades will rotate at the same speed as the motor rotates.
On both direct drive and belt drive fans the motor has two bearings.
Unlike the belt driven fans in case of a direct drive fan there is lesser energy loss.
Direct drive or belt drive.
In the former the motor connects to the fan wheel with nothing in between.
Direct drive fans have no power transmission loss since the propeller is directly connected to the motor shaft.
Greater efficiency is the biggest pro of direct drive fan configurations.
The two bearings on direct drive fan motors which are 7 horsepower and larger are typically regreaseable.
This is because of the fact that the amount of friction is greatly reduced in case of this fan when the fan is operating.
While both belt and direct drive fans have been around for a long time the mainstay fan for most industrial fan applications under 250 hp has been the belt drive fan.
On a direct drive fan as implied by the name the fan propeller is connected directly to the shaft of the motor.